Female reproductive anatomy
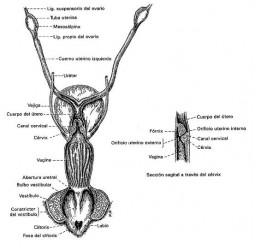
The reproductive system of dogs and humans are very similar. In the female, the reproductive system is composed of the ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix, and vagina. The ovaries are the site of production of the unfertilized eggs, and many of the hormones responsible for heat cycles and the maintenance of pregnancy. The eggs pass from the ovaries into the oviducts. These small finger-like tubes are the site of fertilization by the sperm. From there the eggs pass into the uterus, which is composed of the left and right horn and uterine body. The developing embryos mature within the uterus, attached to its walls by the placenta which also surrounds them.

External organs
Vulva.- is the external urogenital dog hole, is formed of two lips forming a dorsal and ventral corner, which have a smooth muscle.
Clítoris.- is the counterpart of the penis into the female, is located in the clitoral fossa, its function is sexual stimulation.
Internal organs
Vagina vestibule.- is the portion extending from the vulva to the vagina, on the floor of the lobby in the cranial urethra area is also in the vaginal and buccal cingulum region, a place where you will find the bulb buttons penis.
Vagina.- variable length is long, ends in the deepest part of a cul de sac or fornix (to be filled in semen). Its function is the copula.
Cervix.-is a fibromuscular hole separating the uterus from the vagina when bitches are in estrus it is open and allows the entry of sperm. During pregnancy and out the estrous moemnt it remains closed.
Uterous.- is bicornual LMP, with a short body and two long horns arranged in a V. Its function is the transport of eggs and sperm, accommodation and nesting of the zygotes, gestational carrier; sustained by mesometrium. Oviductos.- are tubular structures that serve as communication between the ovary and uterus are composed of three parts: Infundibulum (senses when the egg is released from the ovary), ampulla.